Modern lighting technologies, including LED lights, have transformed how we think about illuminating spaces by offering superior energy efficiency, longevity, and customization options compared to traditional light sources like incandescent bulbs or fluorescent lights.
However, choosing the right lighting for your home or workspace requires understanding key terms like Kelvin, Watts, Lumens, Color Temperature, and CRI (Color Rendering Index). In this guide, we’ll define each term and explain how to select the perfect lights for different environments.

Key Terms for Lighting:
Here’s a quick reference to the essential terms for understanding lighting:
- Kelvin (K): The unit that measures the color temperature of light. It determines whether the light appears warm (yellowish) or cool (bluish).
- Watts (W): The unit of power consumption. Unlike incandescent bulbs, watts in LEDs do not indicate brightness — they represent energy used.
- Lumens (lm): The measurement of the light output or brightness of a bulb. The higher the lumens, the brighter the bulb.
- Color Temperature: Refers to the visual tone of the light based on its Kelvin measurement. It affects the overall mood and uses of the light.
- CRI (Color Rendering Index): A scale from 0 to 100 that indicates how accurately a light source displays colors compared to natural sunlight. Higher CRI values result in better color accuracy.
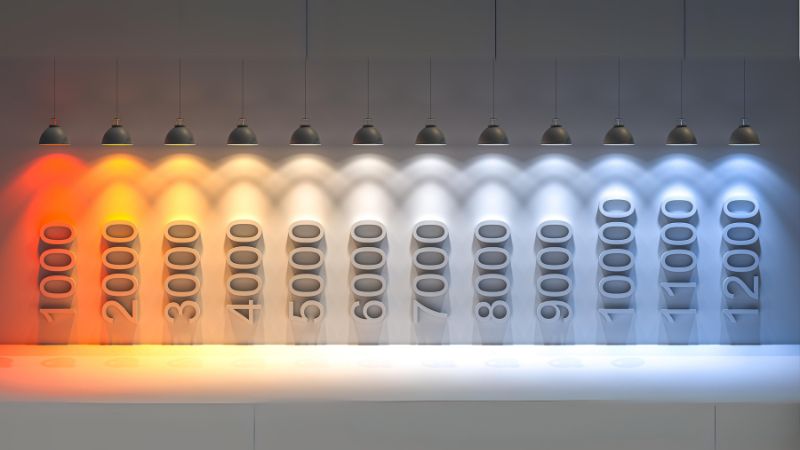
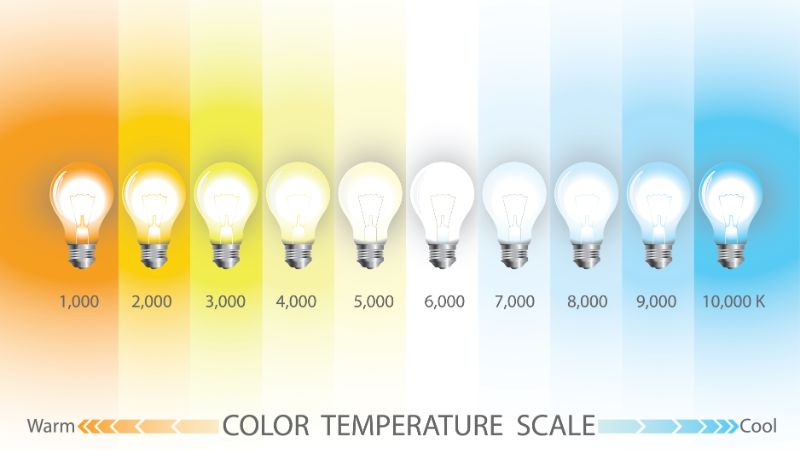
Kelvin and Color Temperature Explained
Kelvin (K) measures the color temperature of a light source and reflects how the light’s color looks. Lower Kelvins (like 2700K) appear “warm” with a yellowish tone akin to old incandescent bulbs, while higher values (e.g., 5000K+) produce “cooler” light that is more bluish. Color temperature plays a crucial role in creating the right ambiance or functional lighting for any space.
Kelvin Scale and Common Applications:
- Warm Lighting (2700K – 3000K): Delivers a soft, yellowish glow reminiscent of traditional incandescent bulbs. It creates a cozy and inviting atmosphere—ideal for living rooms, bedrooms, and dining areas.
- Neutral White/Daylight (3500K – 4500K): Neutral or daylight-toned lighting offers balanced light that isn’t too warm or cool, making it suitable for spaces where both relaxation and activity take place. Great for basements, hallways, and multi-purpose rooms.
- Cool Lighting (5000K – 6500K): Produces a bluish, bright-white light that enhances focus and clarity, essential for task-specific rooms like offices, kitchens, garages, and workshops.
Why Color Temperature Matters:
The right color temperature can profoundly change the mood and function of a room:
- Warm lighting tends to promote relaxation and is often used in casual areas.
- Cool lighting enhances concentration and is better suited for workspaces and areas that require high visibility for detail-oriented tasks.
By selecting the appropriate Kelvin range, you can tailor the atmosphere of each room—relaxing and ambient in the living room and sharp and bright in the kitchen.
Watts vs. Lumens: Energy Use and Brightness
One of the biggest changes with lighting is distinguishing between Watts and Lumens.
- Watts measure the energy consumption of a lightbulb.
- Lumens measure the brightness or total light output.
In traditional incandescent bulbs, people often relied on watts to judge brightness—higher watts meant more light. This is no longer true for LED lights. For LEDs, low wattage doesn’t mean low brightness because LEDs use less energy to produce the same amount of light.
For example:
- A 10W LED bulb can produce the same brightness (about 700 lumens) as a traditional 60W incandescent bulb while consuming far less energy.
Here’s how to think about lumens instead of watts when choosing LED bulbs:
Suggested Lumens per Room:
- Living Room: 1,500 – 2,000 lumens for general lighting.
- Bedrooms: 1,000 – 1,500 lumens for comfortable lighting.
- Kitchens: 2,700 – 4,000 lumens for task visibility and safety while cooking.
- Bathrooms: 1,700 – 3,500 lumens for clarity but not overwhelming brightness.
- Workspaces: 500 – 1,600 lumens for desk lighting or spot illumination where focused intensity is needed.
When choosing LED lights, focus on lumens for brightness and watts for energy efficiency. The goal is to get the most lumens for the least amount of watts—this is where LEDs really shine compared to incandescent lights.

Lumens and Kelvin: Are They Related?
While lumens (brightness) and Kelvin (color temperature) are both used to describe lighting, they are independent properties. That means:
- You can have a light that is warm (2700K) but very bright (high lumens).
- Similarly, you can have a cool (5000K) light that is dim (low lumens).
For example:
- A warm-toned LED at 2700K could emit 1000 lumens, making it bright but still soft and yellowish.
- Alternatively, a 5000K cool-toned bulb could emit only 500 lumens, giving it a blue-white hue but less overall brightness.
Being aware of this distinction helps you better match lighting to specific uses—whether you want a dim, ambient light or a bright working environment.
CRI: Understanding Light’s Ability to Show True Colors
CRI (Color Rendering Index) measures how accurately colors appear under lighting compared to how they look under natural sunlight. A CRI score of 100 represents perfect color accuracy, while lower numbers indicate poorer color reproduction.
Most LED bulbs fall into the 80-90 CRI range, which is adequate for everyday household use. However, certain environments benefit from high CRI lighting:
- CRI 90+ is important for areas where color accuracy is critical—like kitchens (more true-to-life food colors), bathrooms (natural skin tones), makeup studios, art spaces, or high-end retail.
Though CRI is a useful metric, it shouldn’t be the only factor when choosing a light source. Other elements such as color temperature (Kelvin) and brightness (lumens) also play a role in how well lighting performs in various environments.
How is CRI measured?
CRI is calculated by comparing how accurately a light source renders eight standardized color samples (Test Color Samples, TCS) compared to a reference light, typically natural sunlight or a light with a CRI of 100. The closer the light source matches the reference, the higher the CRI score.
Here’s a general breakdown of how CRI is measured:
- Test Samples: Eight pastel color samples (TCS 1-8) are illuminated using both the test and reference light sources. Additional samples (R9-R15) can be included for deeper, saturated colors, like red.
- Color Comparison: The color differences between how the samples appear under the test and reference lights are measured to determine the color shift.
- CRI Calculation: The average of these differences gives the CRI score, ranging from 0 to 100, with higher scores indicating better color accuracy.
To measure CRI, a spectroradiometer is used to capture the spectral output of the light source and compute color accuracy. A CRI of 80-90 is suitable for most applications, while areas requiring precise color accuracy, like art galleries or medical facilities, should aim for 90+ CRI lighting.

Choosing the Right Lighting Solution Step-by-Step
To select the best light, consider three factors: Lumens (brightness), Kelvin (color temperature), and CRI (color accuracy). Here’s a simple guide to help you:
- Start with Lumens: Determine the optimal brightness based on the room’s function. Use more lumens in rooms where visibility is crucial (kitchen, bathroom) and fewer lumens in relaxing spaces (bedroom, living room).
- Choose Kelvin: Decide the ambiance. Use warm lighting (2700K-3000K) in cozy spaces like bedrooms and living rooms, and neutral to cool lighting (4000K-6500K) where clarity and productivity are key.
- Check CRI: Prioritize CRI in rooms where color perception matters. A CRI of 90 or higher is ideal for kitchens, makeup stations, and creative spaces.
Energy Efficiency: Why Watts Still Matter
While lumens dictate brightness, comparing watts can help you choose lights that are energy efficient. The true strength of LEDs is their ability to provide high lumen output with very low power consumption.
Here’s a basic comparison:
- A 7W LED can produce the same brightness as a 50W incandescent bulb.
As a result, switching to lower-wattage LED bulbs helps cut down your electricity bills while providing the same, if not better, lighting quality.
Home Décor and Lighting Design
Beyond functionality, Kelvin and CRI also impact your home’s décor and how you experience color and texture. Here are some recommendations based on room type and design elements:
- Warm Lighting (2700K – 3000K) enhances warm tones, wood finishes, and earthy color palettes. It’s ideal for rooms meant for relaxation, such as living rooms, dining rooms, and bedrooms.
- Cool Lighting (5000K – 6500K) emphasizes crisp lines and modern minimalism and works well in task-oriented spaces. Cool lighting complements modern, industrial, and minimalist styles.
- Neutral Lighting (3500K – 4500K) fits multi-functional spaces where balance is key. Neutral-toned lights blend well with transitional styles that combine both traditional and contemporary elements.
Matching lighting to your design palette can elevate the aesthetic and practical feel of every room.
Final Thoughts
Selecting the right lighting solution requires careful consideration of Lumens (brightness), Kelvin (color temperature), and CRI (color rendering). Together, these factors help you craft a perfect lighting setup that optimizes your home’s beauty, functionality, and energy efficiency.
Make informed decisions that suit each room’s unique needs. From creating a cozy atmosphere in the bedroom to ensuring sharp visibility in the kitchen, your lights can transform the way you see and experience your living space.
Looking for a Reliable LED Lighting Supplier?
For businesses seeking high-quality, energy-efficient, and durable lighting solutions, MF Optoelectronics is a trusted provider. Whether your needs are for commercial, industrial, or specialized lighting applications, MF Optoelectronics offers cutting-edge products and services tailored to meet the unique demands of your business.
To learn more or explore custom solutions, reach out to us today and make an inquiry. Our team is ready to assist with product recommendations, bulk orders, and tailored lighting strategies for your specific projects.





