In our technology-driven world, the demand for reliable power sources is more critical than ever. A standout in this arena is the 18650 battery—a cylindrical lithium-ion battery that has become a cornerstone in powering devices ranging from flashlights to electric vehicles.
This comprehensive guide explores all aspects of 18650 batteries, including their specifications, applications, safety measures, and maintenance tips.

I. What is a 18650 Battery?
Definition and Dimensions
The term “18650” refers to the standardized size of the battery. Here’s how the name breaks down:
- 18: Diameter of the battery in millimeters (18mm)
- 65: Length of the battery in millimeters (65mm)
- 0: Indicates a cylindrical cell
These batteries are a type of lithium-ion (Li-ion) rechargeable battery, renowned for their high energy density, long cycle life, and reliability. Due to their standardized size, they’re widely used in various applications, making them a staple in both consumer and industrial electronics.
Chemical Composition
18650 batteries leverage advanced lithium-ion technology, which provides a high energy density. This means they offer longer battery life and faster charging cycles compared to traditional batteries.
The superior chemical makeup of 18650 cells ensures better performance, making them especially ideal for high-drain devices that require consistent and reliable power.
Common Applications
18650 batteries are integral to a wide range of devices, including:
- Flashlights: High-performance flashlights utilize 18650 batteries for extended run times and bright output.
- Laptops: Many laptops incorporate 18650 cells due to their lightweight nature and efficient power delivery.
- Electric Vehicles: In electric vehicles, 18650 batteries play a crucial role in power management, contributing to overall efficiency.
- Power Tools: Cordless power tools often rely on 18650 batteries for their high discharge rates and durability.
- E-cigarettes and Vapes: These devices use 18650 batteries to handle the high power demands required for vaporizing liquids.
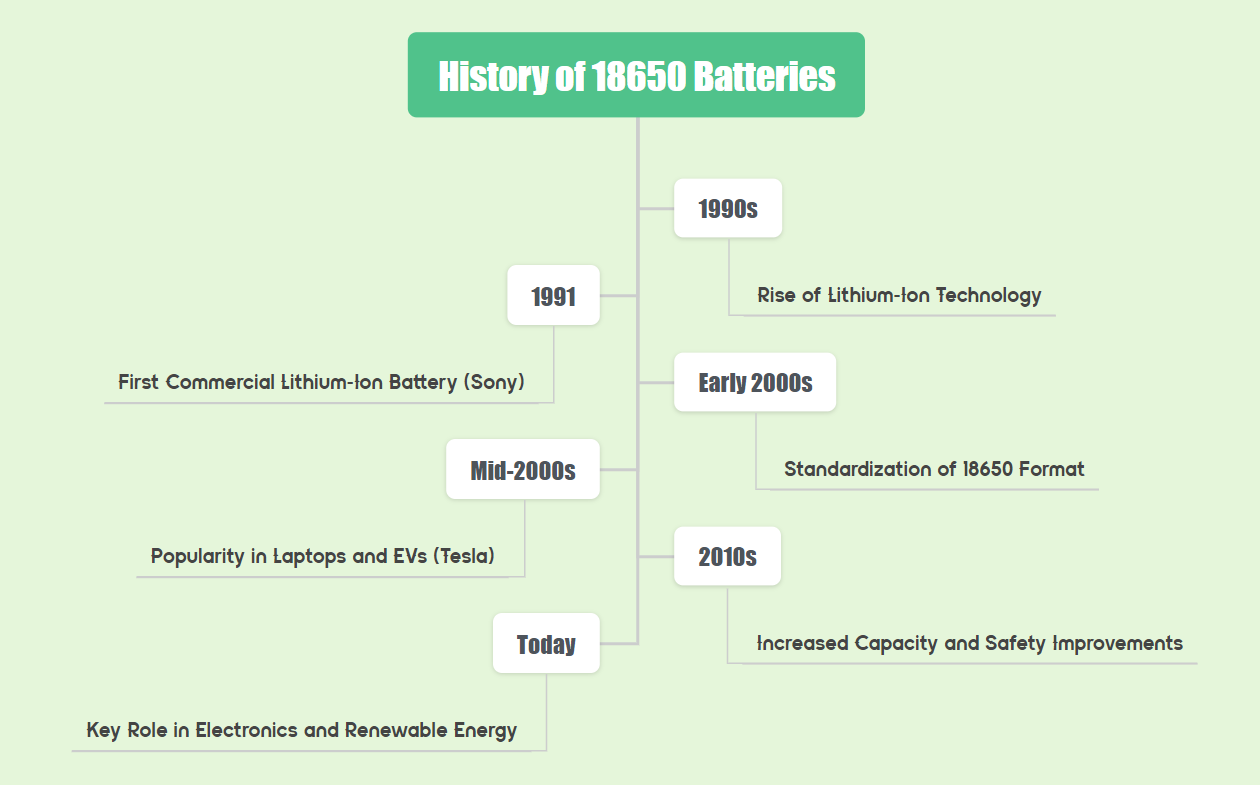
II. History of 18650 Batteries
III. Key Specifications of 18650 Batteries
Voltage Ratings
An 18650 battery typically has a nominal voltage of 3.7V, which can rise to 4.2V when fully charged and drop to around 3.0V when depleted. Understanding these voltage levels is essential for optimizing battery performance and ensuring compatibility with your devices. Operating within the recommended voltage range also prolongs the battery’s lifespan and maintains safety.
Capacity and Performance
Capacity, measured in milliampere-hours (mAh), indicates how much charge a battery can hold. Common capacities for 18650 cells range from 1500mAh to over 3500mAh, depending on the type and manufacturer. A higher capacity means longer run times between charges, which is particularly beneficial for high-drain devices.
Different Types of 18650 Batteries
| Types | Features |
| IMR (Lithium Manganese Oxide) | Offers high discharge rates, ideal for high-drain devices like power tools and vape mods |
| ICR (Lithium Cobalt Oxide) | Known for high energy density, commonly used in laptops and smartphones; however, they have lower discharge rates and may require protection circuits |
| INR (Lithium Nickel Manganese Cobalt Oxide) | Provides a balance between high capacity and high discharge rates, with improved safety features. Widely used due to their versatility |
| IFR (Lithium Iron Phosphate) | Renowned for stability and a longer life cycle, making them suitable for electric vehicles and energy storage systems, albeit with lower energy density compared to other types |
IV. 18650 vs. AA vs. LiPo Batteries
| Feature | 18650 Battery | AA Battery | LiPo Battery |
| Type | Lithium-Ion (Li-ion) | Alkaline / NiMH (Rechargeable) | Lithium Polymer (LiPo) |
| Dimensions | 18mm diameter x 65mm length | 14mm diameter x 50mm length | Varies (Flexible shape) |
| Nominal Voltage | 3.7V | 1.5V (Alkaline) / 1.2V (NiMH) | 3.7V (Single cell) |
| Capacity (Typical) | 1500mAh to over 3500mAh | 1800mAh to 2800mAh (NiMH) | 1000mAh to 5000mAh (varies widely) |
| Rechargeable | Yes | NiMH are rechargeable; Alkaline typically not | Yes |
| Discharge Rate | High | Moderate | Very High |
| Common Applications | Laptops, flashlights, electric vehicles, power tools, e-cigarettes | Remote controls, flashlights, toys | Drones, RC vehicles, and various high-performance devices |
| Size & Weight | Heavier and larger compared to AA | Lightweight and compact | Varies; generally lightweight |
| Safety | Good, especially with protection circuits | Good, with lower risk of fire | Moderate; must be handled with care to avoid puncturing, overcharging |
| Cycle Life | Long (up to 1000 cycles) | Moderate (around 500 cycles for NiMH) | Moderate to long (depends on care and usage) |
| Cost | Usually more expensive than AA | Relatively low-cost | Can be expensive, depending on capacity and brand |
| Environmental Impact | Rechargeable; less waste over time | Rechargeable (NiMH) reduces waste, but alkaline are not recyclable | Generally less eco-friendly, recycling options limited |
V. Charging and Maintenance Tips
How to Charge 18650 Batteries Safely
To charge 18650 batteries safely:
- Use a High-Quality Charger: Always use a charger designed specifically for lithium-ion cells. Features to look for include:
- Overcharge Protection
- Short-Circuit Prevention
- Reverse Polarity Detection
- Charge at Recommended Current Levels: Typically around 0.5C to 1C of the battery’s capacity. For example, a 2000mAh battery should be charged at 1000mA to 2000mA.
- Avoid Cheap, Generic Chargers: These may lack necessary safety mechanisms, potentially leading to battery damage or hazards.
Storage Guidelines
Proper storage significantly impacts the longevity of 18650 batteries:
- Temperature: Store batteries in a cool, dry environment, away from direct sunlight or heat sources, to prevent degradation.
- Charge Level: For long-term storage, charge the batteries to about 40-60% of their capacity. This minimizes the risk of capacity loss over time.
- Protection: Use non-conductive containers or battery cases to prevent accidental short circuits.
- Periodic Checks: If stored for extended periods, check the batteries every few months and recharge if necessary to maintain the optimal charge level.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Monitor your 18650 batteries for signs of trouble:
- Swelling or Bulging: Indicates internal damage; discontinue use immediately.
- Leaking Fluid: A sign of a compromised cell; handle with care and dispose of properly.
- Excessive Heat: If a battery becomes very hot during use or charging, it may be faulty.
- Reduced Performance: Significant drops in capacity or runtime could signal the end of the battery’s life cycle.
If you notice any of these issues, stop using the battery and dispose of it according to local regulations for battery recycling or hazardous waste.

VI. Safety Features
Protected vs. Unprotected Cells
18650 batteries come in two main types:
- Protected Cells:
- Integrated Circuit Board: Safeguards against overcharging, over-discharging, overheating, and short circuits.
- Size: Slightly longer due to added circuitry.
- Recommendation: Ideal for most users, especially in devices without built-in protection.
- Unprotected Cells:
- No Built-In Safety Features: Smaller and lighter.
- Usage: Intended for devices that have their own protective circuitry or by experienced users who understand the associated risks.
Safety Precautions When Using 18650 Batteries
To ensure safe usage:
- Avoid Extreme Temperatures: Do not expose batteries to heat sources or leave them in hot environments.
- Prevent Short Circuits: Never carry loose batteries in pockets or bags with metal objects; use protective cases.
- Use Appropriate Chargers: Only charge with chargers compatible with lithium-ion batteries and rated for your battery’s specifications.
- Do Not Overcharge or Overdischarge: Remove batteries from the charger once fully charged and avoid draining them below the recommended voltage.
- Inspect Regularly: Check batteries for damage, wear, or deformities.
- Proper Disposal: Dispose of old or damaged batteries at designated recycling centers.
- Follow Manufacturer Guidelines: Adhere to any specific instructions provided by the battery or device manufacturer.
Understanding 18650 batteries is essential for making informed decisions. By learning about their specifications, applications, and proper handling techniques, you can improve their performance while reducing potential risks.
Always choose high-quality batteries from reputable brands and follow safety guidelines. This approach will not only extend the lifespan of your batteries but also enhance the safety and efficiency of your devices.

Looking for Lighting Products Equipped with 18650 Batteries?
If you are looking for a supplier of lighting products that are equipped with 18650 Batteries, MF Optoelectronics is a good choice. We specialize in a range of innovative products that utilize reliable 18650 battery technology. Whether you need solutions for consumer electronics, renewable energy systems, or industrial applications, MFopto has you covered with cutting-edge designs and superior performance.
Explore our offerings and feel free to contact our friendly customer service for recommendations or advice.
Detachable Magnetic Lamp with Motion Sensor
Professional Grade LED Portable Search Light
2-In-1 Torch and Lantern with Hanger
Remote-Controlled Tent Light with Colorful String Lights
FAQs:
1. How long does it take to charge a 18650 battery?
Charging time depends on the battery’s capacity and the charger’s output. Typically:
- Standard Chargers (0.5 A): 5–10 hours
- Fast Chargers (1 A): 3–5 hours
2. How can I Charge My 18650 Battery without a Charger?
Charging without a dedicated charger is not recommended due to safety risks. If necessary, consider using:
- USB Lithium-Ion Chargers
- Battery Holders with Built-in Circuits
Always ensure proper voltage and safety measures are in place.
3. What is the lifespan of an 18650 battery?
An 18650 battery typically lasts:
- 300–500 charge cycles
- 3–5 years of calendar life
Proper usage and storage can help extend its lifespan.
4. Are there different sizes of 18650 batteries?
No, “18650” refers to a standardized size:
- Diameter: 18 mm
- Length: 65 mm
However, they vary in capacity, discharge rates, and chemistry.
5. How Long Do 18650 Batteries Last?
In use: A 3000 mAh 18650 battery can power a device drawing 500 mA for about 6 hours.
Overall lifespan: Typically 300–500 charge cycles or 3–5 years.
6. How to Discard Batteries Safely?
To dispose of 18650 batteries safely:
- Cover Terminals: Use non-conductive tape to prevent short-circuiting.
- Use Recycling Programs: Take them to local recycling centers or retail drop-offs.
- Follow Local Regulations: Adhere to your area’s disposal laws.
Never incinerate or throw them in regular trash.







